For hepatitis C-related resources and information, click on the Patients or Health Care Providers tabs.
General information on viral hepatitis
Hepatitis is a general term meaning inflammation of the liver. Although there are many forms of hepatitis,
it is most commonly caused by viruses: hepatitis A, B, C, D, and/or E.
Key facts include:
- each type of hepatitis has different ways of spreading and different symptoms
- hepatitis can be self-limiting, healing on its own, or can progress to scarring of the liver.
- hepatitis is acute when it lasts less than six months and chronic when it persists longer
- a blood test is necessary to diagnose hepatitis
- treatments for hepatitis will depend on the type
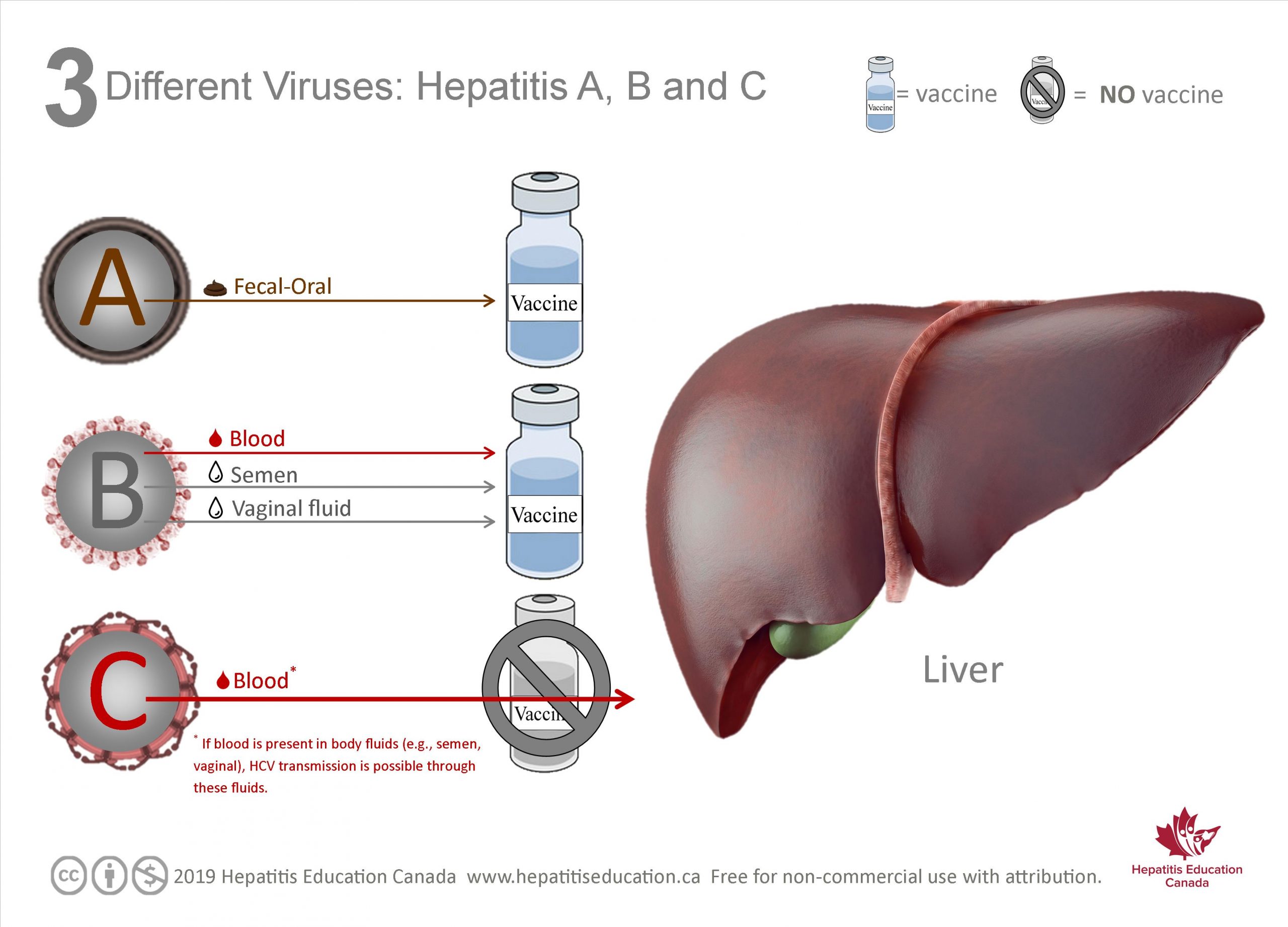
Know your A, B, C’s
In Canada, the most common types of hepatitis viruses are hepatitis A, B and C. These three viruses can be passed to other people, but are spread in different ways. The common* ways these viruses are spread are:
- Hep A is spread through feces (fecal-oral)
- Hep B is spread through blood, semen and vaginal fluid
- Hep C is spread through blood
Other facts to remember:
- Hep A** has a vaccine, but is a self-limited disease – most people resolve the infection within a short period of time
- Hep B has a treatment that can help to limit liver damage, but no cure.
- Hep C has a Cure,*** but no vaccine
___________________________________
*Hepatitis C transmission happens via blood contact, and may be possible through sexual transmission if blood is present, especially in HIV co-infected, MSM and people with multiple sex partners.
**Hepatitis A does not become chronic (the virus does not stay in the body for life) but infections can result in mild or severe illness.
***Hepatitis C treatment is expensive and not everyone qualifies for drug coverage. Overall cure are higher than 90%. Cure rates vary by genotype and previous treatment experience.